Call for a Quick Estimate Today:
(702) 438-9708
 Common Name:
Common Name:
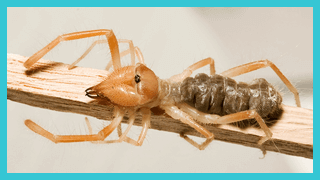
Wind Scorpion, Sun Spider, Camel Spider
Scientific Name:
Eremobates species
Order and Family:
Solifugae, Eremobatidae
Pest Control Service Recommendation:
Scorpion Exterminator
Description:
Their hairiness and rounded opisthosoma (abdomen) are spiderlike, while the front appendages somewhat resemble those of a scorpion. Body length is 1/2″ to 2″ (10-50 mm). The chelicerae (first pair of appendages) are large, toothed, jawlike pincers, and the leglike pedipalps (second pair of appendages) have suctorial tips for seizing prey. Unique racket-shaped organs (malleoli) on the hindmost legs may be sensory.
Food:
Insects, and some smaller animals such as lizards are many times larger than the predator.
Life Cycle:
Females lay eggs in a burrow they dig in the sand. They will lay about fifty eggs at a time and guard them with veracity until they hatch. The small wind scorpions are active only at night, while the adults are more active at night but will also hunt and move around in daylight hours. Most species thought to have only one generation per year.
Habitat:
Primarily in arid to desert regions, (one species in Florida). Most abundant in Africa, particularly in the Horn of Africa.
Range:
California to West Texas and as far north as North Dakota and adjacent areas of Canada.
Discussion:
Wind scorpions are predators, but they have no poison to help them catch their prey. They are very aggressive hunters, stalking and capturing prey in their arms rather than with poison. They eat insects and some smaller animals such as lizards who are many times larger than the predator. Wind scorpions live independently of each other, and only the females with young will live in a group. They are very often regarded as beneficial because they feed on insects and can keep homes insect-free. The wind scorpions’ appearance is quite fierce, yet they are perfectly harmless to man.


Professional, Commercial & Residential Pest Control
Pet & kid friendly, Safe, Organic, Natural Pest Control